A strong and healthy heart is the foundation of overall well-being. One of the most effective ways to strengthen your cardiovascular system is through cardio exercises to improve heart health. These exercises increase your heart rate, enhance blood circulation, and boost stamina while supporting weight management. Whether you’re a beginner or someone with some experience, incorporating the right cardio routines into your weekly schedule can dramatically reduce the risk of heart disease, improve energy levels, and promote a healthier lifestyle. In this fitness guide, we will explore the types, benefits, risks, and practical tips for effective cardio workouts that protect and strengthen your heart.
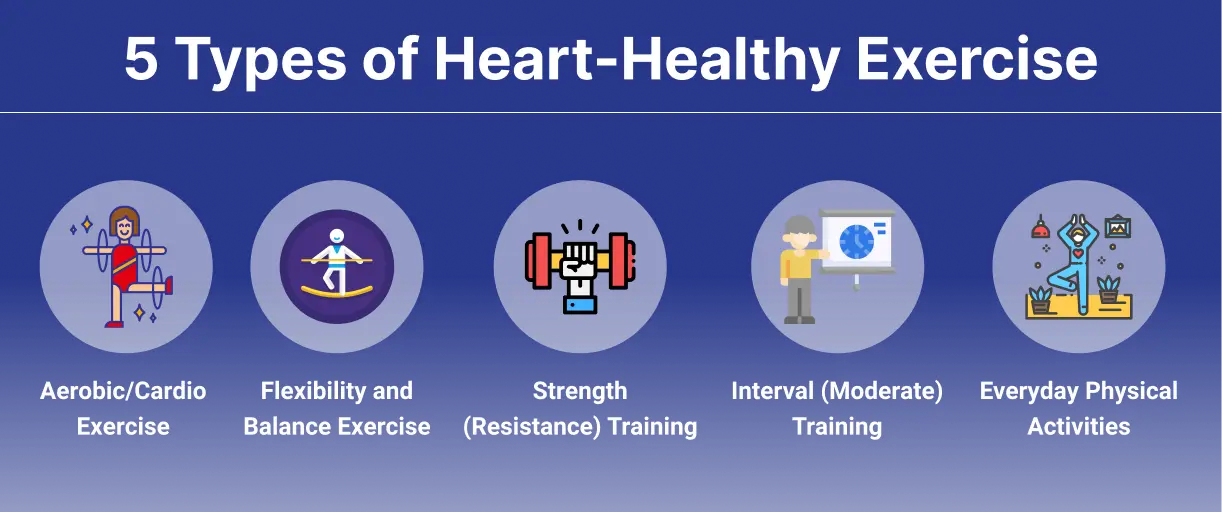
What is Cardio Exercises to Improve Heart Health?
Cardio exercises to improve heart health are physical activities that elevate your heart rate and breathing for a sustained period. Also known as aerobic exercises, these workouts primarily target the heart, lungs, and circulatory system. Unlike strength training, which focuses on building muscle mass, cardio enhances endurance and cardiovascular efficiency.
Common examples include walking, jogging, cycling, swimming, dancing, and aerobic classes. The intensity can vary based on your fitness level, and even moderate activities like brisk walking contribute significantly to heart health. Cardio exercises not only help burn calories but also improve oxygen supply to the body, regulate blood pressure, and maintain healthy cholesterol levels. They form a crucial part of a balanced fitness routine aimed at overall longevity and vitality.
Why is Cardio Exercises to Improve Heart Health Important?
Heart disease remains one of the leading causes of death globally, and lifestyle factors play a major role in preventing it. Engaging in cardio exercises to improve heart health has multiple benefits:
- Strengthens the heart muscle: Regular cardio makes the heart pump blood more efficiently.
- Reduces risk of cardiovascular disease: Lowers blood pressure, cholesterol, and triglyceride levels.
- Improves lung capacity: Enhances oxygen delivery to muscles during daily activities.
- Aids weight management: Burns calories, supporting fat loss and healthy body composition.
- Boosts mood and energy: Releases endorphins that improve mental health and reduce stress.
Even moderate cardio routines performed consistently can lower the risk of heart attacks, strokes, and other chronic diseases. For beginners, starting slow and gradually increasing intensity is key to long-term success.
Detailed Step-by-Step Guide
Step 1: Assess Your Fitness Level
Before starting any cardio routine, evaluate your current fitness:
- Measure resting heart rate
- Note endurance by walking or jogging a short distance
- Check for any medical conditions that may require doctor consultation
Knowing your baseline helps tailor the right exercises without overexertion.
Step 2: Set Clear Goals
Define what you want to achieve with your cardio routine:
- Improve stamina
- Reduce cholesterol or blood pressure
- Lose weight or maintain healthy weight
- Boost overall cardiovascular health
Clear goals make it easier to track progress and stay motivated.
Step 3: Choose Suitable Cardio Exercises
Beginners:
- Brisk walking: 30–45 minutes, 3–5 times per week
- Low-impact cycling: 20–40 minutes, 3 times per week
- Light aerobic classes or swimming
Intermediate:
- Jogging or running: 20–30 minutes, 4–5 times per week
- Interval training: Alternating between moderate and high intensity
- Dance workouts or Zumba sessions
Step 4: Create a Structured Routine
A well-rounded cardio program combines frequency, duration, and intensity:
- Frequency: 4–6 days per week
- Duration: 20–60 minutes per session depending on intensity
- Intensity: Use the talk test—moderate cardio allows conversation, high-intensity limits speech
Sample weekly routine for beginners:
- Monday: Brisk walk (30 minutes)
- Wednesday: Cycling (25 minutes)
- Friday: Swimming (30 minutes)
- Saturday: Light aerobics or dance (20–30 minutes)
Step 5: Warm-Up and Cool-Down
Proper warm-up prepares your heart and muscles, while cool-down aids recovery:
- Warm-up: 5–10 minutes of light jogging or dynamic stretches
- Cool-down: 5–10 minutes of walking followed by static stretches
This reduces the risk of injury and improves performance.
Step 6: Monitor Your Progress
Track key metrics to ensure improvements:
- Resting heart rate
- Exercise duration and intensity
- Weight and body composition changes
- Blood pressure and cholesterol levels
Adjust routines if you hit a plateau or feel your heart rate isn’t increasing appropriately during workouts.
Benefits of Cardio Exercises to Improve Heart Health
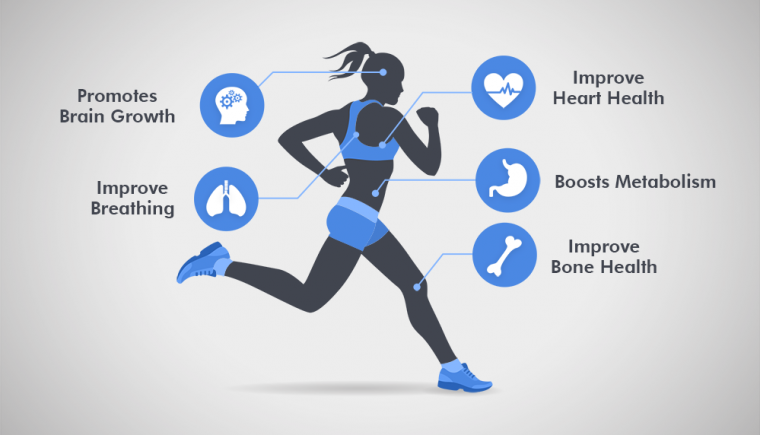
- Strengthens heart and lungs
- Lowers risk of cardiovascular disease
- Supports weight management and fat loss
- Improves circulation and oxygen delivery
- Boosts energy and reduces fatigue
- Enhances mental health and mood
- Promotes longevity and better quality of life
Disadvantages / Risks
- Overtraining can lead to joint or muscle injuries
- High-intensity cardio may strain beginners or those with heart conditions
- Ignoring proper form may cause back or knee problems
- Dehydration if not drinking enough water during exercise
- Burnout if exercise is too frequent without rest days
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Skipping warm-up or cool-down
- Exercising too intensely too soon
- Focusing only on one type of cardio
- Ignoring hydration and nutrition
- Not listening to your body and pushing through pain
- Comparing progress with others instead of individual goals
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. How often should I do cardio for heart health?
Aim for 4–6 days a week, combining moderate and high-intensity sessions depending on your fitness level.
2. How long should each session last?
Beginners should start with 20–30 minutes, while intermediates can aim for 45–60 minutes per session.
3. Can I do cardio at home?
Yes, exercises like jumping jacks, running in place, high knees, and dancing are effective at home without equipment.
4. Is running better than walking?
Both are beneficial. Walking is ideal for beginners, while running adds intensity and burns more calories.
5. Should I combine cardio with strength training?
Absolutely. Strength training complements cardio by building muscles and improving metabolism, which supports heart health.
6. How do I avoid injuries during cardio?
Use proper footwear, warm up, start slow, maintain correct posture, and listen to your body.
7. Can cardio lower cholesterol?
Yes, regular cardio improves HDL (good cholesterol) and lowers LDL (bad cholesterol) and triglycerides.
8. How soon will I see improvements in heart health?
Improvements like better stamina and lower resting heart rate can be noticed in 3–6 weeks with consistent cardio.
Expert Tips & Bonus Points
- Mix intensities: Combine moderate and high-intensity sessions for maximum heart benefits.
- Track heart rate: Use a monitor to ensure you stay in the target zone.
- Stay hydrated: Drink water before, during, and after workouts.
- Use proper form: Avoid slouching while running or cycling to protect joints and back.
- Listen to your body: Take rest days if you feel fatigued or sore.
- Add variety: Cycling, swimming, and dance prevent boredom and target different muscle groups.
- Pair with healthy nutrition: Cardio works best when combined with a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, lean protein, and whole grains.
Conclusion
Incorporating cardio exercises to improve heart health is one of the most effective ways to boost longevity and overall wellness. Whether you’re a beginner or at an intermediate level, a consistent routine of aerobic activities strengthens the heart, reduces disease risk, improves circulation, and enhances mental and physical energy. Combining different cardio exercises, maintaining proper intensity, and integrating strength training can maximize benefits. Remember to start gradually, warm up and cool down, and listen to your body. Over time, these habits become a lifestyle, leading to a healthier, stronger heart, better stamina, and improved quality of life. Commit to regular cardio, stay consistent, and enjoy the long-term rewards of a vibrant, healthy heart.